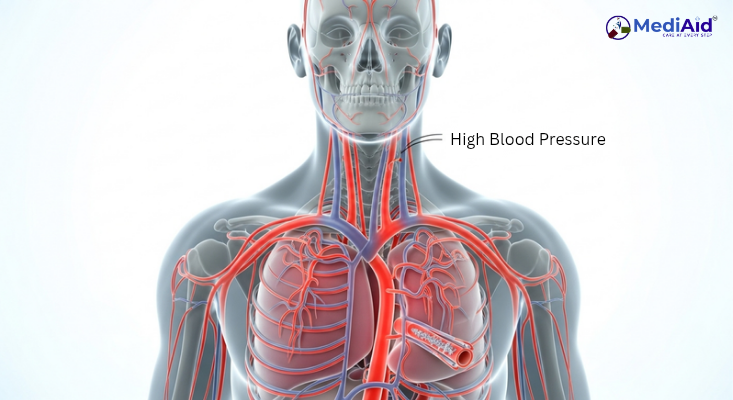
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a condition where the force of blood against the artery walls remains consistently elevated¹. It increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems².
Causes
- Narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis)³
- Obesity and lack of physical activity¹
- Excessive salt intake and high alcohol consumption²
- Stress and genetic factors²
Risk Factors
- Age over 40 years¹
- Family history of hypertension⁴
- Sedentary lifestyle²
- Smoking and heavy alcohol use¹
Symptoms
Hypertension is often called the "silent killer" because it may not cause obvious symptoms. However, some people experience:
- Headache¹
- Dizziness²
- Shortness of breath³
- Nosebleeds (in severe cases ¹
Complications
- Heart attack and heart failure²
- Stroke²
- Kidney disease³
- Vision loss¹
Diagnosis
- Regular blood pressure measurement using a sphygmomanometer¹
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring²
- Blood and urine tests to assess related organ damage³
Prevention
- Healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables²
- Regular physical activity¹
- Stress management techniques³
When to See a Doctor
- Blood pressure consistently above 140/90 mmHg¹
- Severe headaches, chest pain, or difficulty breathing²
- Signs of organ damage, such as swelling or vision changes³
References
- Mayo Clinic
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)