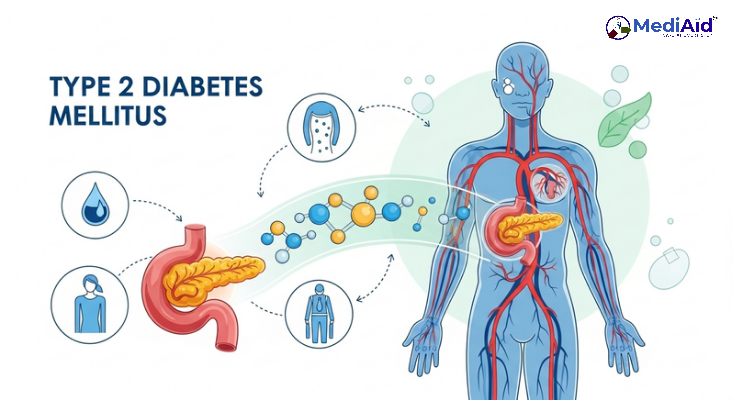
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels¹. It typically develops gradually and is often associated with lifestyle factors and genetic predisposition².
Causes
- Insulin resistance in muscle, fat, and liver cells³
- Inadequate insulin production by the pancreas¹
- Genetic and environmental factors combined with unhealthy lifestyle habits²
Risk Factors
- Overweight or obesity¹
- Sedentary lifestyle²
- Family history of diabetes⁴
- Age over 45 years¹
- History of gestational diabetes³
Symptoms
Common Symptoms:
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)¹
- Frequent urination (polyuria)⁴
- Increased hunger (polyphagia)²
- Fatigue¹
Severe Symptoms:
- Slow-healing wounds¹
- Frequent infections²
- Blurred vision⁴
Complications
- Cardiovascular disease²
- Kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy)³
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)¹
- Eye damage (diabetic retinopathy)²
- Foot ulcers potentially leading to amputation⁴
Diagnosis
- Fasting blood glucose test¹
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test²
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)³
Lifestyle Measures:
- Healthy diet with controlled carbohydrate intake¹
- Regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week)²
- Weight management and maintenance⁴
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy body weight²
- Engaging in consistent exercise¹
- Consuming a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins³
When to See a Doctor
- Persistent fatigue, excessive thirst, or frequent urination¹
- Slow-healing wounds or recurring infections²
- Blurred or sudden changes in vision⁴
Which Doctor to Consult in Bangladesh
1. Diabetologist / Medicine Specialist – Best for initial diagnosis, blood sugar control, and regular follow-up.
2. Endocrinologist – Recommended for complex, uncontrolled, or long-standing diabetes cases.
(Optional: Ophthalmologist or Cardiologist may be consulted if complications arise, but these two doctors are sufficient for most patients.)
References
1. Mayo Clinic
2. World Health Organization (WHO)
3. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)